Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary malignant tumor of liver that has a very high incidence in Asia especially Japan. Other places like Taiwan Penghu, Shanghai (china) have high incidence of liver cancer. There are generally 2 pathological types of hepatocellular carcinoma. The 2 pathological types are fiberlamellar vs non-fibrolamellar (most common type).
- Fibrolamellar: This is not associated with Hepatitis B, C or Cirrhosis.
- Nonfibrolamellar (most common) and associated with cirrhosis from alcoholics, hepatitis B and C.
Etiology and association of Hepatocelluar Carcinoma: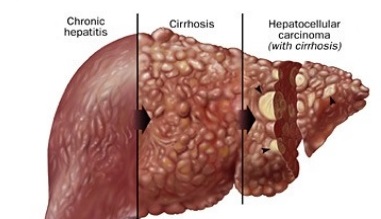
Table of Contents
- Cirrhosis causing risk factors that eventually lead to hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Wilson Disease, Hemochromatosis, alpha-1-anti-trypsin deficiency
- Alcohol, Chronic Hepatitis B/C cause mutation with integration of viral DNA
- Coinfection with HCV and HBV has also been associated with an increased risk of HCC than individual infection alone.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), Primary or secondary biliary sclerosis
- Hepatic adenoma (10% chance of transformation to HCC)
- Aflatoxin B1 (carcinogen found in fungus) called aspergillus that induce p53 mutation which is a guardian tumor suppressor gene.
- Schistosomiasis parasite infection can also cause liver cancer.
- Protectibbe factors: consumption of white meat and statin use has been associated with decreased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Pathogenesis of Liver Cancer from HBV and HCV infection
- The pathogenesis is believed to be from hepatocyte damage and rapid cellular turnover from healing in a cronic inflammatory setting caused by chronic hepatitis B or C infection.
- The imbalance in microenvironment of liver and cytokines of livers infected with the hepatitis C virus, and ultimately causing cirrhosis.
- Poorly differentiated hepatocytes likely proliferate and develop into dysplastic nodules and HCC
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
- Painful hepatosplenomegaly, fatigue, jaundice,cCachexia weight loss
- Cirrhosis complications symptoms are common: Portal hypertension symptoms (ascites, palmer erythema, esophageal varices, hemorrhoids, etc)
- Paraneoplastic syndrome : Increased RBC, Platelets, Calcium, Carcinoid syndrome, hypoglycemia, increased cholesterol, hypertrophic pulmonary osteodystrophy.
Diagnosis of hepatocellular cercinoma
- Liver biopsy – most accurate diagnosis of liver hepatocellular cercinoma
- pathology can be unifocal or multifocal with diffuse infiltration
- Paler than surrounding parenchyma cells
- Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) elevation – useful screening tool and monitor response to treatment.
- Cirrhosis patient need screening for hepatocellular cercinoma via ultrasound (US) and AFP levels every 6 months.
Complications and Progression
- Hepatocellular cercinoma have the tendency for hematogenous spread to other areas.
- May lead to Budd Chiari Syndrome that occlude/thrombosis in the IVC, hepatic vein.
Treatment and Management
- The mainstay of treatment is surgical resection but most of the patients are not eligible due to metastasis or underlying liver dysfunction.
- Other treatment modalities include: Liver transplantation (if diagnosed early and able to get on the list). Others include: radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation, percutaneous ethanol or acetic acid ablation, Radioembolization, transarterial chemoembolization, Cryoablation, radiation therapy and stereotactic radiotherapy.
- Systemic chemotherapy and targeted therapies with molecular agents are currently being studied.
- The specific treatment option depend on both the disease extend and the severity of underlying liver disease, which limits the tolerance to any therapy.
- For patients with cirrhosis, the Child-Pugh classification is used to stratify patients according to their underlying liver disease. Sometimes other measures are increasingly used.